cervical quadrant compression test|lhermitte's sign vs spurling test : member club The Spurling Test is designed to reproduce symptoms by compression of the affected nerve root. The cervical extension is used to induce/reproduce posterior bulging of the . Resultado da Nacionalidade: Camarões. Altura: 1,91 m. Posição: Centroavante. Agente: ROGON. Seleção: Camarões. Jogos de Seleção/Gols: 73 / 20. 3,00 mi. € .
{plog:ftitle_list}
First up in our Casimba review for Canada is the bonuses and offers. Online casinos offer welcome bonuses, free bets, and free spins as a way to draw new players to the site. .
The Kemp test (also known as the quadrant test and extension-rotation test) is a provocative test useful for diagnosing pain related to facet joint pathology, e.g. osteoarthritis. The client performs combined extension and rotation of the .
This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients with cervical radiculopathy and other upper extremity nerve pathologies. ICF Domain (s): Body structure and function. ICF Categories: .
The Spurling Test is designed to reproduce symptoms by compression of the affected nerve root. The cervical extension is used to induce/reproduce posterior bulging of the .
The Spurling test helps to diagnose cervical radiculopathy. It’s also called the Spurling compression test or Spurling maneuver. Cervical radiculopathy occurs when a nerve .
Doctors routinely use the Spurling test to check for cervical radiculopathy, which is the medical term for a compressed or pinched nerve in the neck. Cervical radiculopathy is common.
The Spurling test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy. By reproducing or worsening symptoms through specific . If you think you have a pinched nerve, or cervical radiculopathy, a positive Spurling test can help your doctor with a diagnosis. The Spurling test has been proven to be .Spurling's test involves compression of the cervical spine while it is slightly extended, rotated, and tilted toward one side. In a positive test, pain radiates distally, usually in a radicular .Definition/Description [edit | edit source]. The vertebral artery test (VAT) is used in physiotherapy to test the vertebral artery blood flow to the brain, searching for symptoms of vertebral artery insufficiency and disease.. The test manoeuvre .
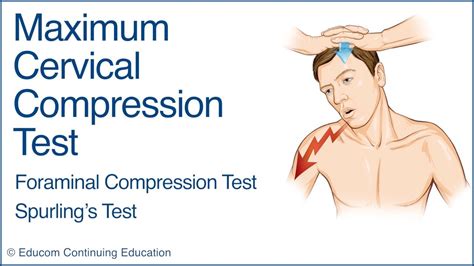
Cervical Spine Tests That Provide or Relieve Pain Spurling Neck Compression Test . Spurling and Scoville first described the Spurling neck compression test, also known as the foraminal compression test, neck .Pages in category "Cervical Spine - Special Tests" The following 11 pages are in this category, out of 11 total. B. Bakody Sign; C. Canadian C-Spine Rule; Cervical Distraction Test; Cervical Flexion-Rotation Test; Cervical rotation lateral flexion test; Cranio‐cervical Flexion Test; H. Hoffmann's Sign; S. Sharp Purser Test; Spurling's Test; T. What is the Spurling test? The Spurling test is a physical assessment to diagnose cervical radiculopathy or a pinched nerve in your neck. If you experience neck pain, a healthcare provider may offer this test.The Spurling test can tell your provider if something is squeezing or pressing against a nerve (nerve root compression) in your cervical spine.
This test is also known by other names, including the Foraminal Compression test and Spurling’s test. This test should not be used if a significant cervical injury is suspected. With the patient in the seated position, tilt and rotate the patient’s neck to the side of involvement. Other names: foraminal compression test, axial cervical compression test, quadrant test. How is the test performed? A doctor applies a downward pressure on the head of a patient who is seated with his/her neck slightly extended backwards and the head tilted to one side (Picture 1). A doctor should release the pressure as soon the patient feels . The Spurling test, also known as the foraminal compression test, neck compression test, or the quadrant test, has been described as highly specific for cervical intraspinal pathologic lesions 9, 10. A study by Shah and Rajshekhar 5 evaluated the test on 50 surgical patients with findings on MRI. The results of the study showed that the Spurling . Thank you for following @OrthoEvalPal Today I will show you how to perform the Cervical Compression Test correctly and what you should see in a positive tes.
Spurling test, maximal cervical compression test, foraminal compression test, neck compression test, quadrant test [Abstract]. (2020).
e36 318ti compression test
Spurling test (foraminal compression test, neck compression test, quadrant test) During World War II, while working at the Walter Reed General Hospital, Roy Greenwood Spurling, the hospital’s first Chief of Neurosurgery and organizer of neurosurgery for the entire Army, first noted this finding in patients with ruptured cervical discs.
This test works when your doctor flexes your cervical spine. If you feel a shock-like pain or feeling down your spine or arms and legs, you’ll get a positive test. Hoffman’s sign.The Hip Quadrant test is a passive test that is used to assess if the hip is the source of a patient's symptoms. . The compression of the femur, through the various ranges, stresses the bone, labrum, cartilage, ligaments, etc. While this test has been labeled as the "hip clearing test," due to the low diagnostic accuracy, it should not .
positive cervical compression test meaning
-Side to side difference in cervical rotation ROM of 10 deg or greater-PAin with PA spring testing of the middle cervical spine 3 positive: Sn .81, Sp .94, +LR 13.5 4 positive: Sn .5, Sp 1.0, +LR infinite Cervical Myelopathy (Cook et al, 2010):-Ataxic gait (+) Hoffman's Test (+) Babinski Test (+) Inverted Supinator Sign-Age > 45 years Flexion compression test. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner stands behind the patient and passively moves the cervical spine into flexion (tilts the patient’s head forward). Then axial compression is applied to .In this test procedure, the cervical spine is fully flexed, in an attempt to isolate movement to C1-C2, which has an unique ability to rotate in flexion. Normal range of rotation motion in end range flexion has been shown to be 44° to each side. In contrast, subjects suffering from headache with C1-C2 dysfunction have an average of 17° less .
The technique for testing the lower cervical spine by this 'quadrant' movement varies appreciably from that used for the upper cervical spine. To test the lower cervical spine for left-sided pain 56 the neck is tilted back into the left corner until the lower cervical spine is fully extended, laterally flexed to the left and rotated to the left .Related to the upper cervical spine, Toby Hall developed a test to determine cervicogenic headache independent of lower cervical spine dysfunction or other types of headache using a C1-2 rotation range test. This has been retested again and again and keeps proving to be helpful in assessing and guiding treatment. Without curiosity and basic .Common names for this test are Spurling’s Neck Compression Test, the Foraminal Compression Test, Neck Compression Test, or Quadrant Test. Takasaki et al noted a reduction in foraminal cross sectional area to approximately 70% of control using the spurling test with 15.4 pounds of axial compressive force as indicated by mri studies. The Spurling test was originally named as Spurling’s neck compression test by the neurosurgeons Roy Glen Spurling and William Beecher Scoville. It was proposed in 1944 for use in the evaluation of “radiculitis.” The test has also been referred to as the Foraminal Compression Test, Neck Compression Test, or Quadrant Test.
The test has also been referred to as the Foraminal Compression Test, Neck Compression Test, or Quadrant Test. The Spurling test is considered a provocative test used in the spinal examination. In several previous trials (mostly conducted in the late 1900’s), the test had proven to have high specificity, but low sensitivity. Cervical Orthopaedic Tests Cervical Palpation Anterior Aspect Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Descriptive Anatomy The sternocleidomastoid muscle extends from the mastoid process of the temporal bone down to the clavicle and sternum (Fig. 3-1). It divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. Its action is to flex the head to the same side and . The maximal side bend "locks out" the lower cervical vertebrae allowing for motion only at the C1-C2 junction. The other method to assess C1-C2, which I learned in PT school at St. Louis University, is the flexion- rotation test. To perform this test, maximally flex the cervical spine followed by maximal rotation either left or right.
in the diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy. Questions/Purposes We assessed the ability of six known variations of the Spurling test to reproduce the complaints of patients diagnosed with cervical radiculopathy. Methods We prospectively enrolled 67 patients presenting with cervical radicular-like symptoms and concordant radiographic findings. Each patient underwent six . What is the cervical quadrant test? The Spurling’s test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy.Supine Transverse Ligament Stress Test: Place one hand on the occiput with the index finger on the space between C2 spinous process and occipital protuberance (where the posterior arch of C1 lies). Place the other hand on the forehead. Lift the head straight up in a vertical plane (not flexion, more of a protraction motion).
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
lhermitte's sign vs spurling test
kemps tests for low back pain
In 70 Kali RM30 FREE. RM168.88. 【LIVE】50% Welcome Bonus. 50%. 【LIVE】10% Daily Bonus. 10%. 【LIVE】5% Unlimited Bonus.
cervical quadrant compression test|lhermitte's sign vs spurling test